In today’s fast-paced business environment, disorganized documents are more than just a nuisance. They represent a significant drain on productivity, a critical security risk, and a genuine barrier to growth. Searching for a misplaced file, using an outdated version of a contract, or failing a compliance audit can cost your business valuable time and money. For small businesses, legal firms, and real estate agencies alike, effective document management is no longer a luxury for large corporations; it’s a foundational pillar for achieving efficiency and operational excellence.
This guide moves beyond generic advice to provide a clear, actionable roadmap. We will explore seven critical document management best practices you can implement today to transform digital chaos into structured order. Following these steps will help secure your sensitive information and empower your team to work smarter, not harder. To truly ‘tame the paper tiger’ and move towards a more efficient future, adopting robust digital document management solutions is essential.
You will learn how to build a scalable system that supports your operations, from establishing foolproof naming conventions and a logical folder hierarchy to implementing robust security and disaster recovery plans. Whether you use a dedicated platform like Superdocu for streamlined collection and validation or refine your existing processes, these strategies will set you up for success. Let’s dive into the practical steps that will make your documents a strategic asset rather than a liability.
1. Implement a Standardized Naming Convention
One of the most foundational document management best practices is implementing a standardized naming convention. This is a systematic approach to naming files that creates consistency across your entire organization. Instead of a chaotic digital folder filled with names like “Final_Report_v2_new” or “meetingnotes,” you establish a clear, predictable structure that makes every document instantly identifiable and searchable.
This practice is crucial because it eliminates ambiguity and saves countless hours that would otherwise be spent searching for misplaced files. When every team member follows the same rules, finding a specific contract, invoice, or client file becomes a matter of seconds, not minutes.
Why This Is a Top Priority
A logical naming system is the bedrock of an efficient document management system. Without it, even the most advanced software can become cluttered and ineffective. It directly impacts productivity, reduces the risk of using outdated document versions, and simplifies employee onboarding by providing a clear framework from day one. This structured approach, advocated by bodies like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), transforms digital chaos into organized, accessible information.
Key Insight: Your file naming convention is not just an IT policy; it’s a core operational process that enhances team collaboration and reduces workflow friction. A document’s name should tell its story before you even open it.
How to Implement a Naming Convention
Creating an effective naming convention involves defining a set of rules and ensuring everyone adheres to them. The goal is to choose elements that are most relevant to how your team searches for and uses documents.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Keep it Simple: Your convention should be easy to understand and remember. Overly complex systems are often ignored.
- Use Dates for Sorting: Start filenames with the date in YYYY-MM-DD format. This automatically sorts files chronologically, which is invaluable for project timelines and financial records.
- Avoid Spaces: Use underscores
(_)or hyphens-instead of spaces. Spaces can cause errors in some systems and web applications. - Be Consistent with Abbreviations: If you use abbreviations (e.g., “INV” for Invoice, “CTR” for Contract), document them in a guide and ensure everyone uses the same ones.
- Include Version Numbers: For documents that undergo revisions, add a version identifier like
_v01,_v02. This prevents confusion and ensures everyone is working on the latest draft.
Industry-Specific Examples:
- Legal Firms:
ClientName_CaseNumber_DocumentType_YYYY-MM-DD- Example:
Smith-J_1123_Motion-to-Dismiss_2023-10-26.pdf
- Example:
- Real Estate Agencies:
PropertyAddress_DocumentType_ClientName_Date- Example:
123-Oak-St_Lease-Agreement_Doe-J_2023-11-15.pdf
- Example:
- HR Departments:
EmployeeID_DocumentType_YYYY-MM-DD_vN- Example:
EMP451_Performance-Review_2024-01-20_v01.docx
- Example:
By establishing and enforcing a clear naming convention, you lay the groundwork for successful document management, making your digital assets more secure, searchable, and valuable.
2. Establish a Hierarchical Folder Structure
Working in tandem with a naming convention, a hierarchical folder structure is another cornerstone of effective document management best practices. This is a logical, tree-like organization system that arranges documents into nested folders based on clear business categories like departments, projects, clients, or time periods. Instead of a single, massive folder, you create an intuitive pathway that mirrors how your organization naturally thinks about and accesses its information.
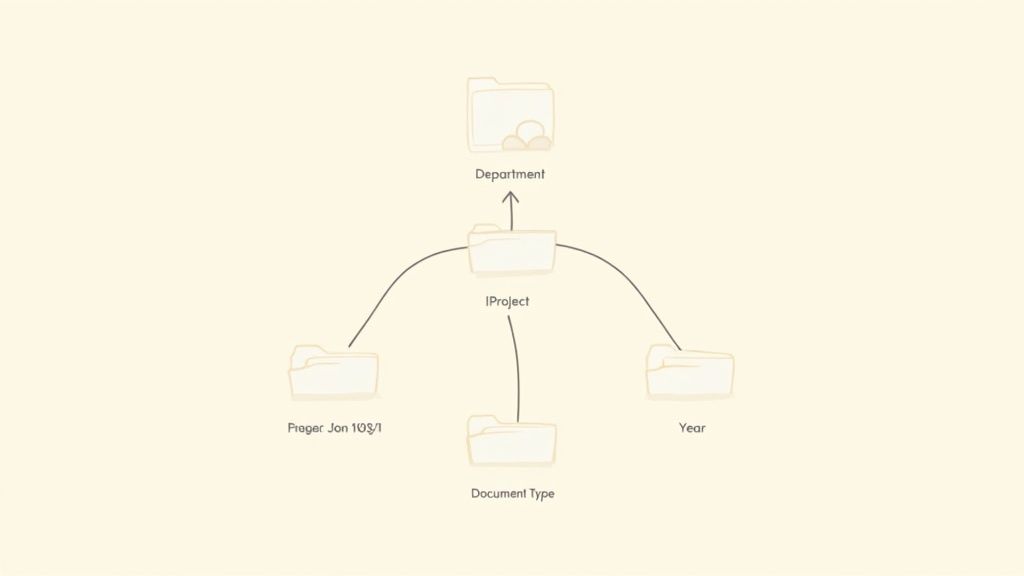
This practice is essential because it provides a map for your digital files. It guides users directly to the information they need without relying solely on search functions. When a logical structure is in place, navigating to a specific project’s invoices or a client’s signed contract becomes a simple, predictable process.
Why This Is a Top Priority
A well-designed folder hierarchy brings order to digital chaos, making your entire document repository browsable and manageable. It prevents the creation of duplicate or “lost” folders and ensures information is stored consistently across all teams. Professional bodies like ARMA International and the Project Management Institute (PMI) champion this approach because it reduces user error, streamlines document retrieval, and simplifies the process of setting access permissions, which is critical for security and compliance.
Key Insight: A folder structure isn’t just about storage; it’s about creating logical pathways. Think of it as the digital equivalent of a well-organized filing cabinet, where every drawer, folder, and divider has a clear purpose.
How to Implement a Folder Hierarchy
Building an effective folder structure means designing it around how your team actually works. The goal is to create a system that feels intuitive and requires minimal training. This involves mapping out the primary categories your business operates on and breaking them down into logical sub-folders.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Limit Folder Depth: Keep your hierarchy relatively shallow, ideally no more than 3 to 5 levels deep. Overly complex structures become difficult to navigate.
- Use Consistent Naming: Apply consistent naming rules to folders, just as you do with files. For example, always use the client name or project number at the same level.
- Create a Structure Map: Document your folder hierarchy in a simple chart or guide. This serves as a reference for existing employees and a training tool for new ones.
- Consider User Workflow: Design the structure to match the steps in your team’s processes. Placing related documents for a specific task in the same parent folder can dramatically improve efficiency. A well-designed hierarchy can supercharge your document management workflow.
- Regularly Review and Optimize: Your business will evolve, and your folder structure should too. Schedule periodic reviews to archive old folders and adjust the structure to meet new needs.
Industry-Specific Examples:
- Consulting Firms:
Client > Project > DocumentType > Year- Example:
Acme-Corp/Q3-Marketing-Campaign/Invoices/2023/
- Example:
- Universities:
Department > AcademicYear > CourseCode > AssignmentType- Example:
History/2024-2025/HIST-101/Syllabi/
- Example:
- Manufacturing:
ProductLine > ProjectPhase > DocumentCategory- Example:
Generators/Alpha-Model/Design/Blueprints/
- Example:
By creating a clear and logical folder hierarchy, you build a scalable foundation that complements your file naming convention, making your digital workspace truly organized and efficient.
3. Implement Version Control and Document Lifecycle Management
Beyond just naming files correctly, one of the most critical document management best practices is implementing version control and managing the entire document lifecycle. This is a systematic approach to tracking document changes, managing multiple drafts, and controlling a file’s journey from creation and collaboration to archival and eventual disposal. It ensures team members always access the most current, approved version, preventing costly mistakes.

This practice is essential for collaborative environments where documents like contracts, proposals, and project plans undergo numerous revisions. Without it, teams risk working from outdated information, leading to confusion, rework, and compliance issues. Effective version control creates a clear audit trail, showing who made what change and when.
Why This Is a Top Priority
Version control is the safety net that protects your organization’s intellectual property and operational integrity. It is mandated by quality management standards like ISO 9001 and is non-negotiable in regulated industries like pharmaceuticals, where every change must be documented for compliance. It eliminates the “Final_Final_v3_USE_THIS_ONE” chaos, replacing it with a reliable, single source of truth. By managing the document lifecycle, you also ensure that sensitive information is securely disposed of when no longer needed, reducing legal and security risks.
Key Insight: Version control is not just about tracking history; it’s about ensuring future accuracy. A document’s lifecycle-from creation to deletion-should be a controlled, auditable process, not an accidental one.
How to Implement Version Control and Lifecycle Management
Implementing this practice requires a combination of technology and process. Modern document management systems often have these features built-in, but establishing clear internal rules is just as important. The goal is to make the process transparent and automatic.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Establish a Clear Versioning Scheme: Use a simple system like
v1.0for major releases andv1.1,v1.2for minor revisions. Document this scheme and train all users on it. - Use Check-In/Check-Out Features: Train employees to “check out” a document to lock it for editing, preventing simultaneous conflicting changes. When they “check in” the file, they can add comments summarizing their updates.
- Automate Approval Workflows: Set up workflows that automatically route documents to the necessary stakeholders for review and approval before a new version is published. To dive deeper into this, you can read our guide on document workflow automation at Superdocu.com.
- Define Retention and Archival Policies: Determine how long different document types must be kept. Set rules to automatically archive old documents and flag them for final deletion after the retention period expires.
- Regularly Audit and Purge: Schedule periodic reviews to clean up obsolete drafts and versions. This keeps your system lean and reduces storage costs.
Industry-Specific Examples:
- Pharmaceuticals:
DrugID_StudyProtocol_v2-1_Approved_YYYY-MM-DD- Example:
XAB-101_Clinical-Trial-Protocol_v3-0_Approved_2023-09-05.pdf(Version control is crucial for FDA compliance).
- Example:
- Software Development: Teams use Git for code, but apply similar principles for technical documentation, tracking changes with commit messages.
- Example:
API-Documentation_v4.2.1.md
- Example:
- Manufacturing:
PartNumber_Quality-Control-Procedure_v1-4_YYYY-MM-DD- Example:
PN-7890_QC-Checklist_v2-1_2024-02-11.xlsx(Ensures workers on the floor use the latest procedure).
- Example:
4. Establish Robust Access Control and Security Measures
A critical document management best practice is establishing a comprehensive security framework. This involves implementing robust access controls to dictate who can view, edit, share, or delete documents. By managing permissions based on user roles, responsibilities, and specific business needs, you protect sensitive information from unauthorized access while ensuring team members can work efficiently.
This practice is essential for safeguarding confidential data like financial records, employee information, and proprietary business strategies. It moves beyond simple password protection, creating a granular system where access is granted on a “need-to-know” basis, which is a cornerstone of modern data security and compliance.
Why This Is a Top Priority
In an era of increasing data breaches and stringent privacy regulations, strong access control is non-negotiable. It is fundamental to regulatory compliance with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA, which mandate the protection of personal and sensitive data. Frameworks like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and ISO 27001 heavily emphasize access control as a core component of information security management, mitigating risks of both internal and external threats.
Key Insight: Security isn’t just about keeping outsiders out; it’s about ensuring insiders only have access to the information necessary for their roles. Proper access control is proactive risk management, not just a defensive measure.
How to Implement Access Control Measures
Implementing effective access control requires a strategic approach that aligns security policies with operational workflows. The goal is to create a secure yet user-friendly environment where data is protected without hindering productivity.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign permissions based on job functions. For example, an HR manager can access all employee files, while a team member can only view their own.
- Use Strong Authentication: For highly sensitive documents, require multi-factor authentication (MFA) to verify user identity beyond a simple password.
- Establish Data Classification: Categorize your documents (e.g., Public, Internal, Confidential, Restricted) and apply security rules accordingly. This ensures the highest level of protection is applied where it’s needed most.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Periodically review who has access to what. Remove permissions for employees who have changed roles or left the company to prevent “privilege creep.”
- Monitor Access Logs: Keep an eye on access logs to detect unusual activity, such as multiple failed login attempts or access outside of normal business hours, which could indicate a security threat.
Industry-Specific Examples:
- Healthcare Organizations:
HIPAA-compliant controls restrict patient record access to authorized medical staff only. - Financial Institutions:
Multi-factor authentication is required to access client investment portfolios or loan applications. - Government Agencies:
Classified document systems use multi-level security clearances to control access based on information sensitivity.
By embedding robust security and access controls into your document management system, you build a foundation of trust and compliance, protecting your organization’s most valuable digital assets.
5. Implement Comprehensive Metadata Management
While a strong naming convention creates an initial layer of order, comprehensive metadata management takes searchability and organization to a completely different level. Metadata is simply “data about data”-it’s the extra information you attach to a file that describes its content, context, and characteristics. This practice involves systematically tagging documents with key details, making them infinitely easier to find, filter, and manage.
Instead of relying solely on a filename, users can search for a document by its author, creation date, client name, project ID, or status. This creates a flexible, multi-dimensional search capability that a simple folder structure cannot match, making it one of the most powerful document management best practices for complex environments.
Why This Is a Top Priority
Metadata transforms your document repository from a simple digital filing cabinet into an intelligent, searchable database. It provides crucial context that filenames alone cannot convey, enabling advanced sorting, automated workflows, and more robust compliance and records management. For industries like legal, finance, and research, where documents are tied to specific cases, clients, or projects, metadata isn’t a luxury; it’s an operational necessity. As pioneered by standards like the Dublin Core Metadata Initiative, structured metadata ensures information remains accessible and valuable long-term.
Key Insight: Metadata is the hidden engine of modern document management. It allows you to ask complex questions of your data, such as “Show me all active contracts for Client X that are due for renewal in the next 90 days,” a search impossible with filenames alone.
How to Implement Metadata Management
Effective metadata management starts with defining which information is most critical for your organization’s workflows. The goal is to capture data that helps you categorize, find, and process documents more efficiently.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Define Essential Fields: Identify the core pieces of information for different document types. For an invoice, this might be
Invoice Number,Client Name,Due Date, andAmount. For an HR file, it could beEmployee ID,Document Type(e.g., contract, review), andHire Date. - Use Controlled Vocabularies: For fields like “Status” or “Department,” use dropdown lists or predefined options (e.g.,
Draft,Pending Approval,Approuvé) instead of free-text fields. This prevents inconsistencies like “Marketing,” “Mktg,” and “marketing dept.” - Automate When Possible: Modern document management systems can automatically extract metadata like creation date, author, and even text from the document itself using OCR technology, reducing manual data entry.
- Make Key Fields Mandatory: Ensure that users cannot save a new document without filling in the most critical metadata fields. This enforces consistency from the start.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Periodically review your metadata to clean up inconsistencies, fill in missing information, and ensure the standards are being followed.
Industry-Specific Examples:
- Legal Firms:
MatterNumber,ClientName,DocumentType(Pleading, Discovery, Correspondence),Author,DateFiled- Example: A paralegal can quickly find all “Discovery” documents related to “MatterNumber 2024-105.”
- Marketing Agencies:
CampaignName,Client,AssetType(Blog Post, Social Graphic, Video),Statut(In Progress, Final),PublishDate- Example: A manager can filter for all assets with “Status: Final” for the “Q4-Holiday” campaign.
- Construction Companies:
ProjectID,BlueprintNumber,Discipline(Electrical, Plumbing, Structural),RevisionDate,ApprovedBy- Example: An engineer on-site can pull up the latest “Plumbing” blueprint for “ProjectID 789B” on a tablet.
By building a robust metadata strategy, you empower your team with advanced search capabilities, streamline workflows, and unlock the true value hidden within your documents.
6. Regular Backup and Disaster Recovery Planning
Beyond organizing your active files, one of the most critical document management best practices is ensuring their long-term survival. This involves creating a comprehensive strategy for regular backups and disaster recovery. It’s a safety net that protects your vital information from loss due to hardware failure, cyberattacks, natural disasters, or simple human error.
This practice is not just about making copies; it’s about ensuring business continuity. A solid plan guarantees that you can quickly restore access to your documents and resume operations with minimal downtime, preserving client trust and protecting your revenue.
Why This Is a Top Priority
In a digital-first world, your documents are valuable business assets. Losing them can be catastrophic, leading to legal liabilities, compliance failures, and irreparable reputational damage. A proactive backup and disaster recovery plan, a concept championed by organizations like the Disaster Recovery Institute International, transforms risk management from a theoretical exercise into a practical, reliable process. It ensures your data remains available no matter what happens.
Key Insight: A backup is only as good as your ability to restore from it. Your disaster recovery plan should be tested, documented, and regularly updated to be effective when you need it most. Don’t just hope for the best; prepare for the worst.
How to Implement a Backup and Recovery Plan
Building a resilient system requires a structured approach to both backing up data and planning for its recovery. The goal is to create redundancy and a clear, actionable plan that can be executed under pressure.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Follow the 3-2-1 Rule: This is the gold standard for backups. Maintain 3 copies of your data, store them on 2 different types of media (e.g., an external hard drive and the cloud), with at least 1 copy kept offsite.
- Automate Everything: Manual backups are prone to human error and forgetfulness. Use automated backup software or cloud services to ensure backups run consistently without daily intervention.
- Test Your Restores: Regularly test your ability to recover files from your backups. This practice identifies potential issues before a real disaster strikes, ensuring your plan actually works.
- Document Recovery Steps: Create a clear, step-by-step guide for restoring data. This document should be accessible even if your primary systems are down (e.g., a printed copy or stored on a separate cloud service).
- Monitor and Alert: Set up monitoring for your backup processes to get alerts for any failures. A backup you assume is running might have been failing for weeks.
Industry-Specific Examples:
- Healthcare Organizations: Implementing HIPAA-compliant, encrypted cloud backup solutions to protect sensitive patient health information (PHI) while ensuring availability for patient care.
- Financial Institutions: Using geographically distributed backup systems, as popularized by AWS and other cloud providers, to ensure that a regional disaster does not impact data availability.
- SMBs: Utilizing cloud storage like Dropbox or Google Drive, which offer built-in version history and multi-data center replication, providing a simple yet powerful disaster recovery solution. To streamline this, you can learn more about how document collection software can integrate with these systems for seamless protection.
By making regular backups and disaster recovery a non-negotiable part of your operations, you safeguard your organization’s most critical assets against any eventuality.
7. Establish Clear Retention and Disposal Policies
A crucial document management best practice is establishing clear retention and disposal policies. This involves creating a systematic schedule that dictates how long specific documents must be kept and when they should be securely destroyed. This practice ensures your organization complies with legal and regulatory obligations while simultaneously managing storage costs and reducing digital clutter.
Without a formal policy, organizations often keep documents indefinitely, which increases risk and expense. A defined lifecycle for every document, from creation to disposal, prevents accidental deletion of critical records and ensures timely removal of outdated, sensitive information, thereby minimizing liability.
Why This Is a Top Priority
Document retention is not just an administrative task; it’s a core component of risk management and compliance. Regulations like the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) and HIPAA mandate specific retention periods for financial and health records. Failure to comply can result in severe penalties, legal challenges, and reputational damage. This process, championed by organizations like ARMA International, helps you confidently navigate the complex web of legal requirements. For instance, proper document management ensures you meet all necessary reporting obligations. For a detailed guide on this, consider learning more about nonprofit reporting requirements.
Key Insight: A document retention policy transforms your data from a potential liability into a managed asset. It’s about knowing not only what to keep and for how long, but also when and how to let go securely.
How to Implement a Retention and Disposal Policy
Developing an effective policy requires collaboration between your legal, compliance, and operational teams to define schedules based on document type and regulatory context. The goal is to create a clear, automated, and defensible process.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Define Retention Schedules: Work with legal counsel to classify documents (e.g., contracts, invoices, employee files) and assign specific retention periods to each category.
- Automate Where Possible: Use your document management system to automatically flag documents for review or disposal once their retention period expires. This reduces manual effort and human error.
- Implement Legal Holds: Ensure your system can place a “legal hold” on documents related to litigation. This overrides the standard disposal schedule to preserve evidence.
- Train Your Team: Educate all employees on the importance of the policy and their role in adhering to it. This is critical for consistent enforcement.
- Use Secure Disposal Methods: When a document reaches the end of its lifecycle, ensure it is disposed of securely. For digital files, this means using digital shredding tools, not just moving them to a trash bin.
- Audit Regularly: Periodically review your retention practices to ensure they are being followed correctly and are still aligned with current laws and business needs.
Industry-Specific Examples:
- Financial Services: A firm subject to SOX must retain audit workpapers for 7 years.
- Policy:
Financial-Audit-Records_Retention-7-Years_Auto-Delete-After-Review
- Policy:
- Healthcare: A hospital following HIPAA guidelines must retain patient records for at least 6 years from the last date of service.
- Policy:
Patient-Medical-Record_Retention-6-Years_From-Last-Service-Date
- Policy:
- Legal Firms: A firm must implement a litigation hold on all documents pertaining to an active case, suspending their normal disposal schedule indefinitely.
- Policy:
CaseNumber_1123_Litigation-Hold_Active
- Policy:
By implementing robust retention and disposal policies, you fortify your compliance framework, reduce storage overhead, and protect your organization from unnecessary risks.
7 Best Practices Comparison Matrix
| Practice | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implement a Standardized Naming Convention | Moderate: requires initial setup and training | Low to moderate: mainly time investment | Consistent, searchable, and organized documents | Organizations seeking document searchability and collaboration | Improves searchability, reduces duplicates, enables compliance |
| Establish a Hierarchical Folder Structure | Moderate: planning and periodic restructuring | Moderate: ongoing maintenance | Intuitive navigation; scalable document storage | Businesses with diverse projects or departments | Supports access control, improves organization, scalable |
| Implement Version Control and Document Lifecycle Management | High: requires software, governance, and training | High: specialized tools and user adoption | Accurate versioning, audit trails, compliance | Teams needing collaboration and auditability | Prevents conflicts, supports compliance, improves quality |
| Establish Robust Access Control and Security Measures | High: complex setup and ongoing updates | High: security tools and monitoring | Secure, compliant, controlled document access | Organizations with sensitive data and regulatory needs | Protects data, ensures compliance, enables secure remote access |
| Implement Comprehensive Metadata Management | Moderate to high: schema design and training | Moderate: tools for metadata capture | Enhanced searchability and automation | Entities requiring advanced document classification | Improves discoverability, automates workflows, supports compliance |
| Regular Backup and Disaster Recovery Planning | High: setup, testing, and continuous management | High: storage and skilled personnel | Document protection and recovery capability | All organizations requiring business continuity | Protects data, ensures continuity, supports quick recovery |
| Establish Clear Retention and Disposal Policies | Moderate: policy design and enforcement | Moderate: compliance and monitoring | Reduced storage costs and regulatory compliance | Organizations with legal and compliance requirements | Lowers costs, minimizes legal risk, improves governance |
From Theory to Action: Building Your Modern Document Strategy
Navigating the landscape of digital information can feel overwhelming, but it doesn’t have to be a chaotic journey. We’ve explored the foundational pillars of effective document management, from creating standardized naming conventions and logical folder hierarchies to implementing robust version control. Each practice serves a distinct purpose, yet they all work together toward a single, powerful goal: transforming your scattered files into a strategic, accessible, and secure asset.
Mastering these concepts is not merely an IT exercise; it is a fundamental business strategy. When you establish clear access controls, you protect sensitive client data and maintain compliance. When you leverage comprehensive metadata, you unlock powerful search capabilities that save countless hours. This systematic approach eliminates the friction and frustration that define disorganized systems, freeing your team to focus on high-value work instead of hunting for misplaced documents.
Your Roadmap to Implementation
Moving from understanding these principles to executing them is the most critical step. The journey from a cluttered, inefficient system to a streamlined one is a process of deliberate, incremental improvements. Don’t feel pressured to overhaul everything overnight. Instead, focus on a phased approach that delivers tangible wins quickly and builds momentum for lasting change.
Here are your actionable next steps:
- Conduct a Quick Audit: Start by evaluating your current system against the seven best practices we discussed. Where are the biggest pain points? Is it a lack of version control causing confusion, or are security protocols too loose? Identifying the most significant gaps will help you prioritize your efforts.
- Focus on One Area First: Choose one high-impact area to tackle initially. For many businesses, implementing a standardized naming convention is a great starting point because it immediately brings a sense of order and makes files easier to locate.
- Empower Your Team with the Right Tools: Manual enforcement of these rules is prone to human error and inconsistency. A dedicated document management platform automates these best practices, making them an integrated part of your workflow rather than an additional chore. Tools like Superdocu are specifically designed to embed these principles directly into processes like client onboarding or vendor management.
- Document and Train: Once you’ve defined your new processes, document them in a clear, accessible guide. Conduct a brief training session to ensure everyone on your team understands the new protocols and, more importantly, the reasons behind them. For a deeper dive into practical implementation, consider exploring specific 7 best practices for document management that can transform your operations.
The Lasting Impact of an Organized System
Ultimately, embracing these document management best practices is an investment in your organization’s future. It’s about building a resilient, scalable framework that supports growth, enhances security, and improves the client experience. Imagine a world where every document request is fulfilled in seconds, compliance audits are stress-free, and your team operates with a newfound sense of clarity and efficiency. This isn’t a distant dream; it’s the direct result of a well-executed document strategy. By taking these deliberate steps today, you are laying the groundwork for a more organized, productive, and secure tomorrow.
Ready to turn these best practices into reality with a tool built for action? Superdocu helps you automate document collection, validation, and management with branded portals and automated reminders, embedding efficiency directly into your workflows. Start your free trial today and experience the future of document management.
